Larger mesh deployments may desire to separate mesh operation from mesh observability. This means deploying Kiali, and potentially other observability tooling, away from the mesh.
This separation allows for:
- Dedicated management of mesh observability
- Reduced resource consumption on mesh clusters
- Centralized visibility across multiple mesh clusters
- Improved security isolation
Deployment Model
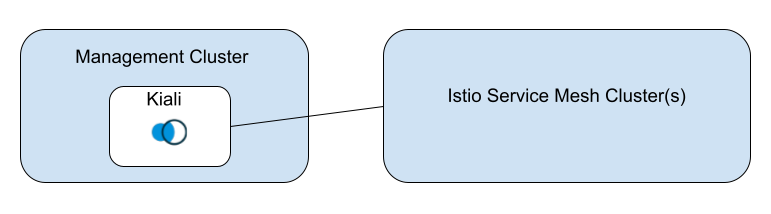
This deployment model requires a minimum of two clusters. The Kiali “home” cluster (where Kiali is deployed) will serve as the “management” cluster. The “mesh” cluster(s) will be where your service mesh is deployed. The mesh deployment will still conform to any of the Istio deployment models that Kiali already supports. The fundamental difference is that Kiali will not be co-located with an Istio control plane, but instead will reside away from the mesh. For multi-cluster mesh deployments, all of the same requirements apply, such as unified metrics and traces, etc.
It can be beneficial to co-locate other observability tooling on the management cluster. For example, co-locating Prometheus will likely improve Kiali’s metric query performance, while also reducing Prometheus resource consumption on the mesh cluster(s). Although, it may require additional configuration, like federating Prometheus databases, etc.
The high-level deployment model looks like this:
Configuration
Configuring Kiali for the external deployment model has the same requirements needed for a co-located Kiali in a multi-cluster installation. Kiali still needs the necessary secrets for accessing the remote clusters.
Additionally, the configuration needs to indicate that Kiali will not be managing its home cluster. This is done in the Kiali CR by setting:
clustering:
ignore_home_cluster: true
Kiali typically sets its home cluster name to the same cluster name set by the co-located Istio control plane. In an external deployment there is no co-located Istio control plane, and therefore the cluster name must also be set in the configuration. The name must be unique within the set of multi-cluster cluster names.
kubernetes_config:
cluster_name: <KialiHomeClusterName>
Authorization
The external deployment model currently supports openid, openshift, and anonymous authorization strategies. token auth is untested and considered experimental.
Metrics Aggregation
For external Kiali deployments, you need a unified metrics endpoint that aggregates metrics from all mesh clusters.